
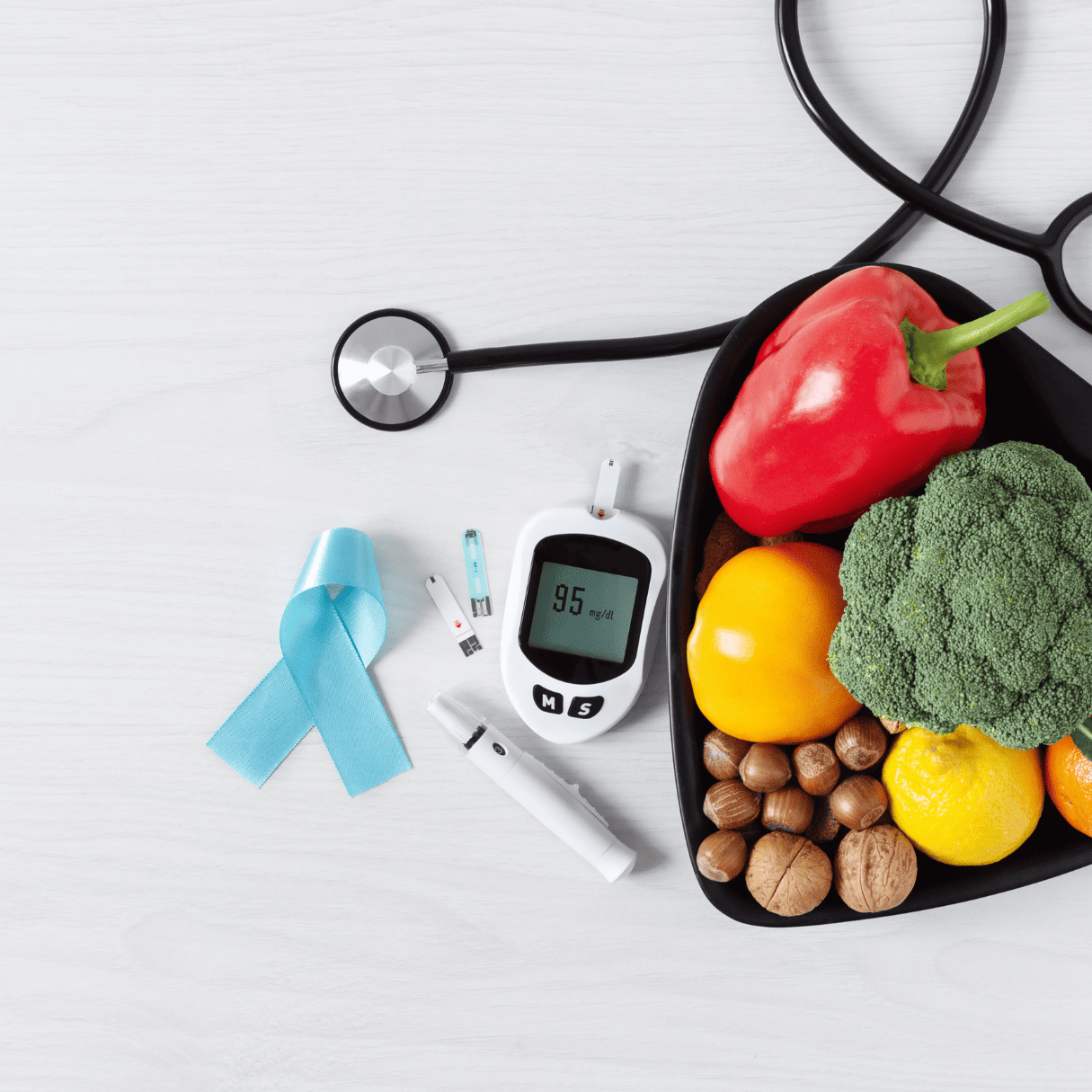
Diabetes is a long-term condition where your body struggles to process sugar properly. This leads to high blood sugar levels because glucose from food isn't converted into energy effectively. Managing diabetes is important to prevent potential damage to your heart, kidneys, eyes, nerves, teeth, and gums.

HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) attacks your immune system, weakening your body’s ability to fight infections and cancers. If untreated, it can progress to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), where the immune system is severely compromised. HIV is primarily spread through unprotected sex, from an infected mother to her child during pregnancy or breastfeeding, and by sharing needles.
Prostate cancer begins in the prostate gland and is the most common non-skin cancer among men worldwide. It is the leading cause of cancer-related death in men over 75. While rare in men under 40, it can develop at any age. If the prostate becomes enlarged, it can press on the urethra, which may slow or block the normal flow of urine.

Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome is associated with mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, which help prevent uncontrolled cell growth. Inheriting a mutation in these genes raises your risk of breast, ovarian, and other cancers, but only 5–10% of breast cancer cases and 10–15% of ovarian cancer cases are due to these mutations.
This guide outlines the types of drug tests, how to choose the right one, and when to use them. Drugs are categorised as prescribed medications, like benzodiazepines and opiates, or illicit drugs, such as amphetamines, cocaine, and marijuana. Prescription drugs can be misused, and those doing so may exhibit specific signs. Drug testing is performed when abuse is suspected, using screening tests to identify negative results and confirmation tests for positive results to specify the drug or check for false positives. The most common screening test is an immunoassay, which can be done quickly at the point of care or in a lab.

The Ebola virus causes a serious illness characterized by severe bleeding. Since its discovery in 1976, it has led to small outbreaks in countries like the Democratic Republic of Congo, Sudan, and Ivory Coast. Currently, there is a significant outbreak in West Africa that began in December 2013. As of August 7, 1711 individuals have been affected, with 932 reported deaths. The outbreak is primarily impacting Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone, with three cases also reported in Nigeria.
Mumps is caused by a virus and spreads from person to person through tiny droplets of saliva or mucus from the mouth, nose, or throat of an infected individual, usually when they cough, sneeze, or talk. It can also spread indirectly if someone touches objects or surfaces that an infected person has touched without washing their hands and then rubs their mouth or nose. Being mindful of these transmission methods can help you protect yourself and others.
The Faecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) is a simple, non-invasive test that checks for hidden (occult) blood in your stool. It is a non-invasive way to screen for colorectal cancer, as the presence of blood in the stool may indicate polyps or cancer in the colon or rectum.

Cholesterol is a waxy substance essential for your body, helping with cell function, nerve insulation, hormone production, and digestion. However, high cholesterol levels can increase your risk of heart disease. Lowering your cholesterol can help reduce this risk and improve heart health.

It is possible to test HIV negative while your partner tests positive, a situation known as being serodiscordant, which can occur in both long-term relationships and single encounters. Several factors influence whether someone contracts HIV, including the type of sexual activity, overall health, and the use of protection, which may explain why you have not been infected.

Breast cancer is a type of malignant tumor that forms in the breast and can spread to other areas of the body. It may also be referred to as breast carcinoma or mammary carcinoma, depending on the specific type. Not all lumps or tumors in the breast are cancerous; in fact, most are benign. To determine whether a lump is cancerous or benign, it’s important to have a medical examination.

Iron is a crucial mineral in every cell, essential for producing hemoglobin, which gives blood its red color and carries oxygen. Iron deficiency anemia happens when there isn't enough iron to make sufficient hemoglobin. Certain groups are more at risk for iron deficiency, including young children due to rapid growth, adolescent girls and women of childbearing age from menstruation, and pregnant women, who need more iron for their increased blood volume and the developing fetus.

A wellness test is a medical evaluation, such as an annual physical checkup, designed to help prevent health issues in individuals who appear healthy. This differs from tests done to diagnose specific symptoms. During wellness tests, your doctor may take blood, urine, or stool samples to assess various substances in your body. Below are some important tests your doctor may recommend. Your doctor will also guide you on how often to have these tests, based on factors like your age, sex, current health status, and risk factors.

Antibiotic resistance happens when bacteria change and become resistant to the antibiotics used to treat the infections they cause.This is compromising our ability to treat infectious diseases and undermining many advances in medicine.
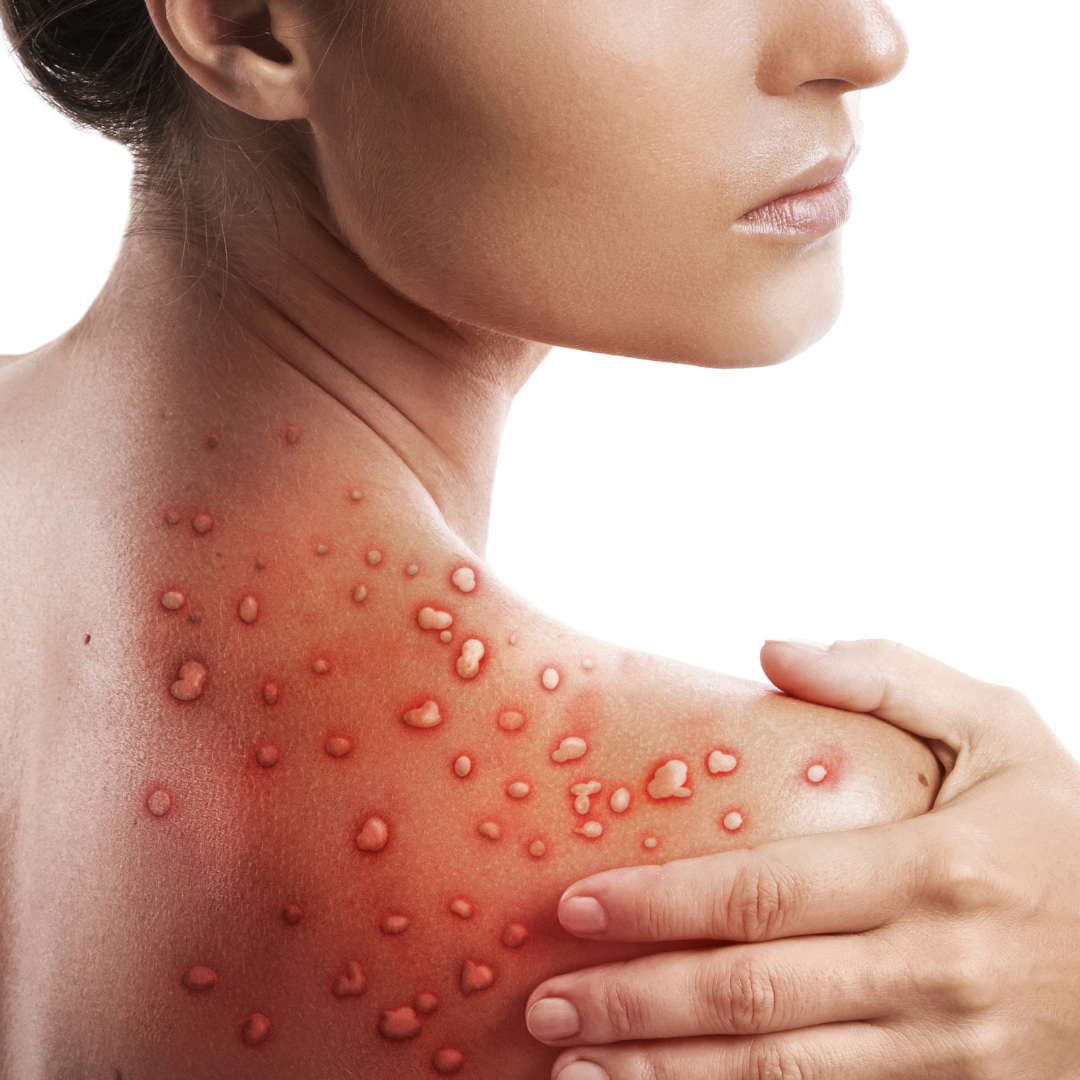
Monkeypox is a rare illness caused by the monkeypox virus, mainly found in West and Central Africa, where it spreads from infected animals to humans and between people. It typically spreads through small droplets released when an infected person breathes out and can also be transmitted through direct contact with skin blisters or contaminated objects like clothing and towels. In rare cases, the virus can be passed from a pregnant woman to her baby in the womb. If you have concerns about monkeypox, please consult your healthcare provider.
Tuberculosis, or TB, is an infection caused by bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. While it can affect any part of the body, it most commonly targets the lungs. TB spreads easily through the air, especially in crowded environments, and you can become infected simply by breathing in the bacteria.
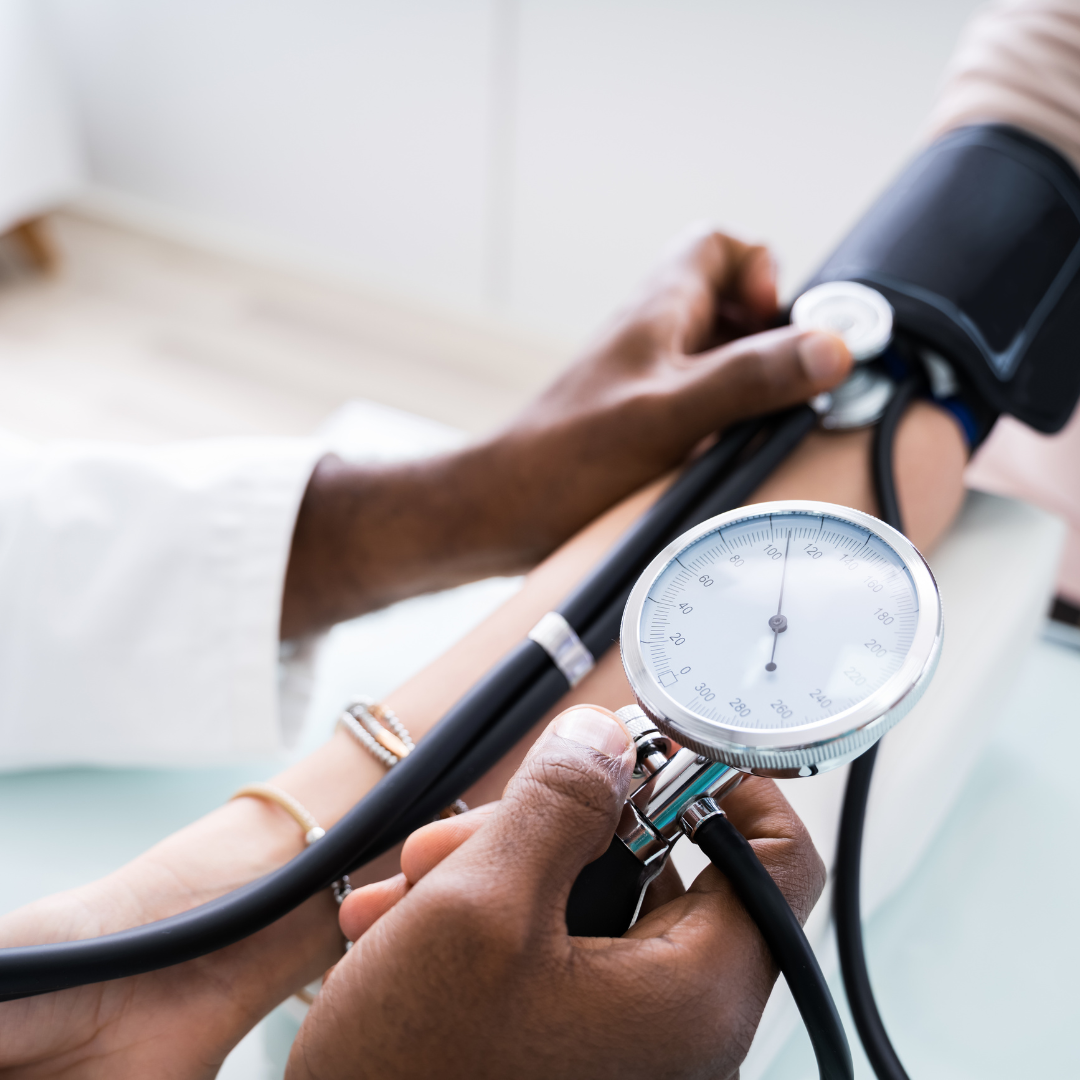
Blood pressure is the force of blood against artery walls as your heart pumps. It’s measured with a cuff around your arm and given as two numbers, like 120/80: the first number (systolic) is when your heart beats, and the second (diastolic) is when it rests. High blood pressure, or hypertension, means your blood pressure is too high, which can damage blood vessels and organs, leading to health problems like heart disease.

Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the main cause of cervical cancer. There are 14 high-risk types of HPV, with types 16 and 18 responsible for over 70% of cases. HPV spreads through close sexual contact and is very common; around 80% of women will be infected at some point. Most women clear the infection on their own, but some may not, increasing their risk of cancer.
Influenza, or the flu, is an infection caused by the influenza virus that affects the nose, throat, and airways. While many viruses can infect the respiratory tract, the flu often leads to more severe illness. Flu viruses cause annual outbreaks, peaking in winter. The two main types that infect humans are influenza A and B, with H1N1 and H3N2 being the current circulating subtypes. H1N1 was first identified in humans in 2009 and has since become a regular seasonal flu subtype. Both H1N1 and H3N2 can cause severe illness and are treated similarly.

If you’re sexually active, especially with multiple partners, it’s important to practice safer sex and get tested regularly for sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Many STIs can be present without symptoms, making testing crucial. The type of tests you need and how often to get screened depend on your age, sexual behaviors, and other risk factors. If you think you need an STI test, talk to your doctor about your concerns. Remember, STI testing isn’t automatically included in routine visits or examinations.
Pregnancy can bring a mix of emotions, and it’s natural to have concerns. Most expectant parents have healthy babies, but some may face a higher risk of genetic conditions. If this applies to you, amniocentesis may be offered to check for potential genetic abnormalities. Amniocentesis involves taking a small sample of amniotic fluid surrounding your baby. This fluid contains cells and substances that can be tested in the lab. Below, we’ll explain when amniocentesis might be recommended, along with its timing, safety, and accuracy, all to support your peace of mind.

Our genes, made up of DNA, are organized into chromosomes, and humans have 23 pairs. While most babies are born healthy, a small number may have chromosomal abnormalities that can affect their health. Some of these can be detected through prenatal testing. There are two main types of prenatal tests: screening tests, which are generally safer but less accurate, and diagnostic tests, which are more accurate but carry higher risks. It’s important to understand your options and choose what feels right for you. If you have questions, please consult your healthcare provider.
Richmond, Johannesburg,
2092